Meet Agentforce: Your New AI Teammate in Salesforce
Today’s customers expect fast, personalized support, making exceptional service not just a nice-to-have but a competitive edge. Salesforce Agentforce is built to help support teams meet that challenge head-on. As part of the Salesforce ecosystem, Agentforce equips agents with smart tools and real-time insights that help agents resolve issues faster and more effectively. It streamlines everyday tasks, reduces manual work, and brings the correct information to agents when needed. This blog will explain what Agentforce offers, how it supports service teams, and why it’s becoming a valuable asset for companies focused on delivering top-tier support.
What Is Agentforce?
Agentforce is Salesforce’s next-generation, AI-powered automation platform designed to create, deploy, and manage autonomous agents that support employees and customers across departments, such as service, sales, marketing, and commerce. Unlike traditional chatbots or scripted tools, Agentforce agents can understand intent, reason through decisions, and take action independently, all while operating within pre-defined business rules and brand guardrails.
Built directly on Salesforce’s core platform, Agentforce integrates seamlessly with tools like Salesforce Flow, Apex, Data Cloud, and the Einstein Trust Layer. This ensures agents can securely access and act on real-time business data from across your organization. Agentforce enables enterprises to scale support and operations through agents that operate 24/7, personalize interactions, and efficiently handle repetitive or time-sensitive tasks.
To simplify agent creation, Agentforce includes three low-code tools:
-
Agent Builder – for designing and deploying autonomous agents with customizable skills.
-
Prompt Builder – for defining how agents interact using natural language.
-
Model Builder – for training agents on business-specific data securely.
Organizations can choose from a library of out-of-the-box agents, such as:
-
Service Agent – replaces chatbots for real-time customer service.
-
Campaign Optimizer – manages end-to-end marketing campaigns.
-
Sales Development Representative (SDR) – nurtures leads and engages prospects.
-
Buyer & Personal Shopper – help customers find, compare, and purchase products.
-
Merchant – supports retail teams with product listings, promotions, and insights.
-
Sales Coach – helps train and upskill sales reps using personalized guidance.
Because Agentforce agents can act autonomously, they’re not restricted to static flows. They adapt to real-time conditions and can trigger processes based on changes in data or customer behavior. If an issue exceeds their scope, they know when to escalate the interaction to a human agent, maintaining a seamless experience.
Core Concepts Behind Agentforce
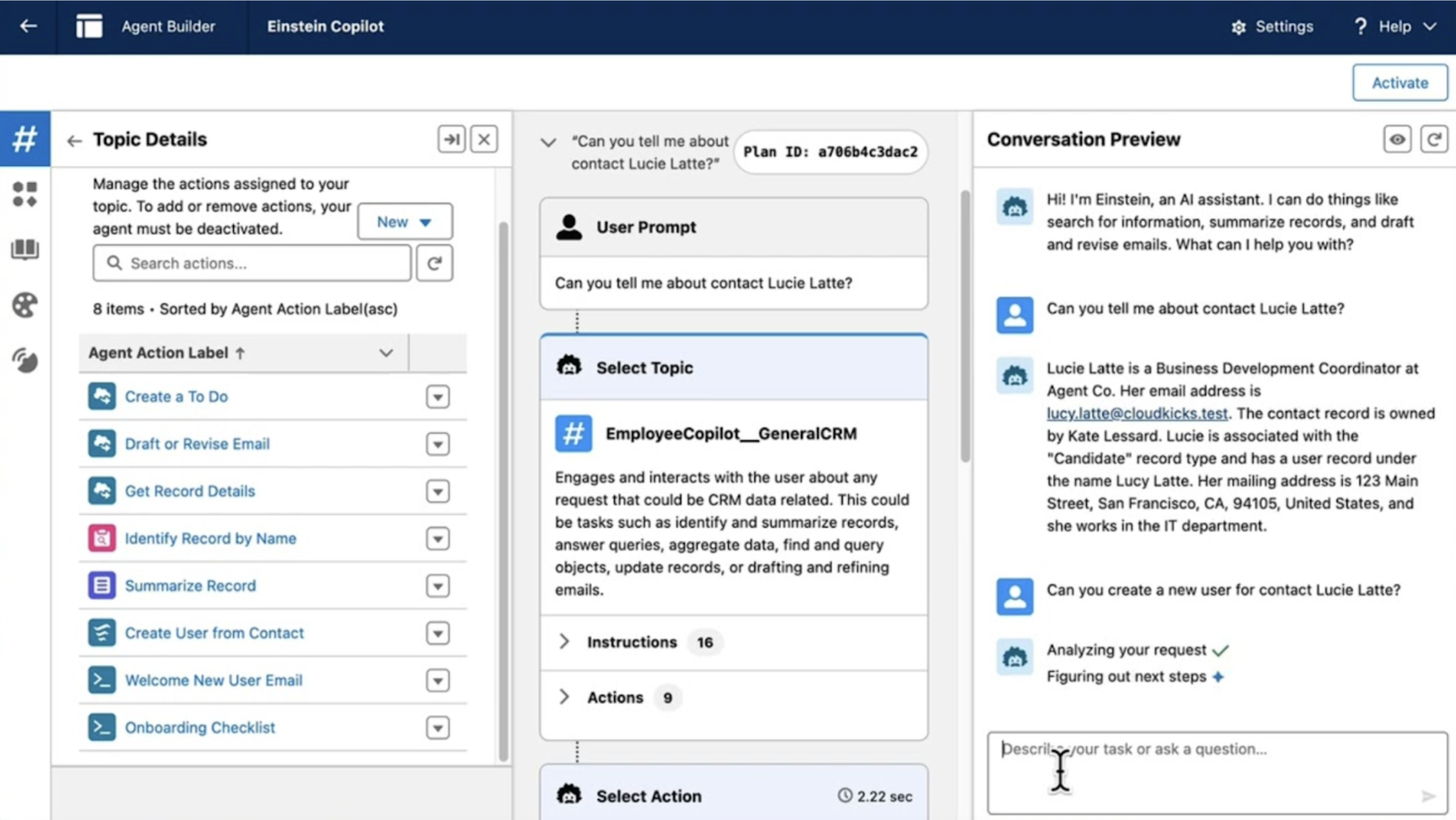
Topics
A Topic defines the use case or conversation pattern the agent supports — essentially, what the agent can help with. Each topic outlines a path the agent follows, including what to say, what to do, and how to respond.
Topics include:
-
Agent Message Step: Introduces the task or asks a question.
-
Action Step(s): Execute logic, such as invoking a Flow or running a query.
-
Agent Response Step: Uses a prompt to summarize the result or next step.
-
Summary Step (Optional): Ends the topic with a wrap-up message.
Each topic starts with a trigger phrase, which is matched to user input. The agent chooses the most relevant topic based on input + reasoning engine evaluation. Topics can also be nested or chained based on output or logic, giving the agent flexibility to follow multi-step conversations.
Instructions
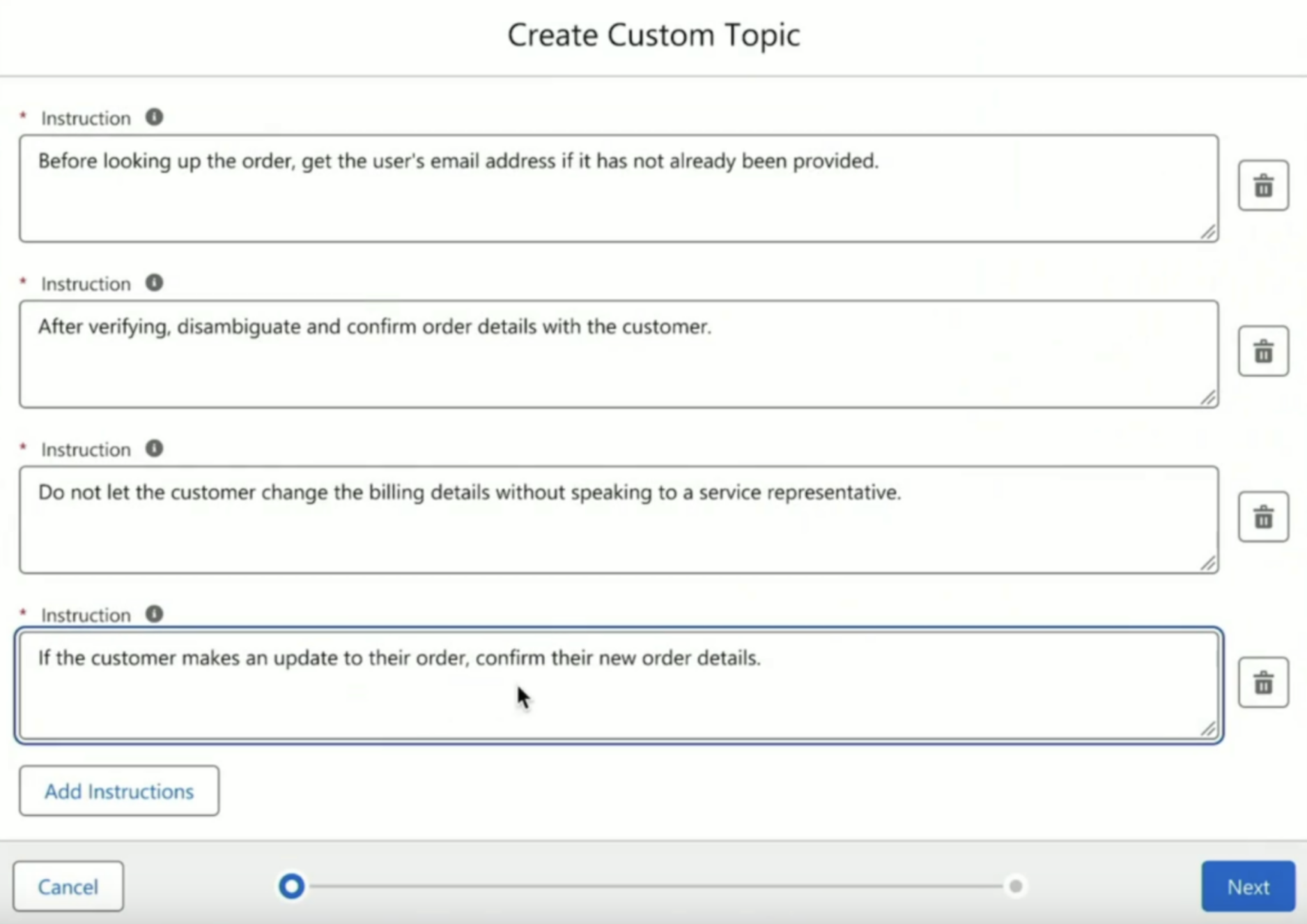
Instructions provide the agent with behavioral guidance. These are high-level rules or directives that influence how the agent behaves across all topics.
Examples:
-
“Never share internal IDs with the user.”
-
“Use the latest Case data when answering.”
-
“Only escalate to human agents for priority accounts.”
Instructions act like guardrails — they don’t control the steps directly but shape how the agent interprets prompts and chooses responses.
Prompts
Prompts are language models’ input templates that help formulate how the agent responds or interprets information. Prompts can be static or dynamic (using variables or data inputs), and they're created in the Prompt Builder.
Prompt usage examples:
-
Clarifying intent: “Ask the user to confirm the account name.”
-
Summarizing actions: “Summarize the case details pulled from the action.”
-
Responding to users: “Here is the latest update on your case: {Case.Status}.”
In Prompt Builder, you can:
-
Use text + merge fields
-
Reference previous steps in the topic
-
Include AI-suggested phrasing
-
Preview how the prompt will behave using test values
Prompts are used in Agent Message, Agent Response, and Summary steps.
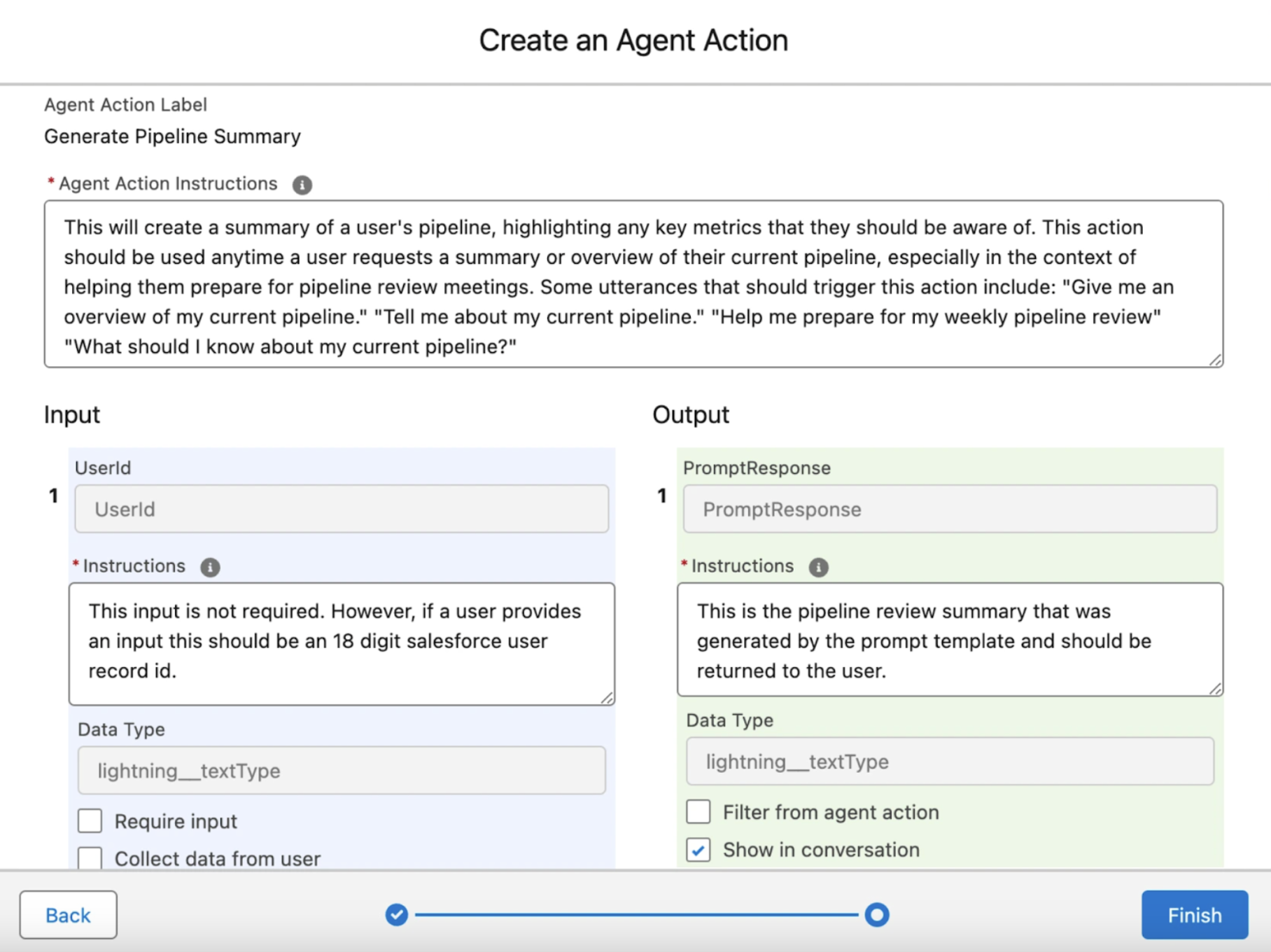
Actions
Actions are reusable functions or logic blocks that an agent can invoke during a conversation. They power the Action Step in a topic, allowing the agent to do something (not just talk).
There are two levels of actions:
1. Inline Actions: Used directly in a topic.
2. Reusable Actions: Created in the Actions tab and referenced across multiple topics.
Types of actions include:
-
Flow (run automation like creating or updating records)
-
Apex Class
-
SOQL Query
-
Data Cloud Query (search across unified customer profiles)
Each action has:
-
Input parameters: e.g., Case ID, email address
-
Output variables: returned values used in prompts or responses
You can also preview/test an Action directly within Agent Builder to validate input/output logic.
Building An Agent
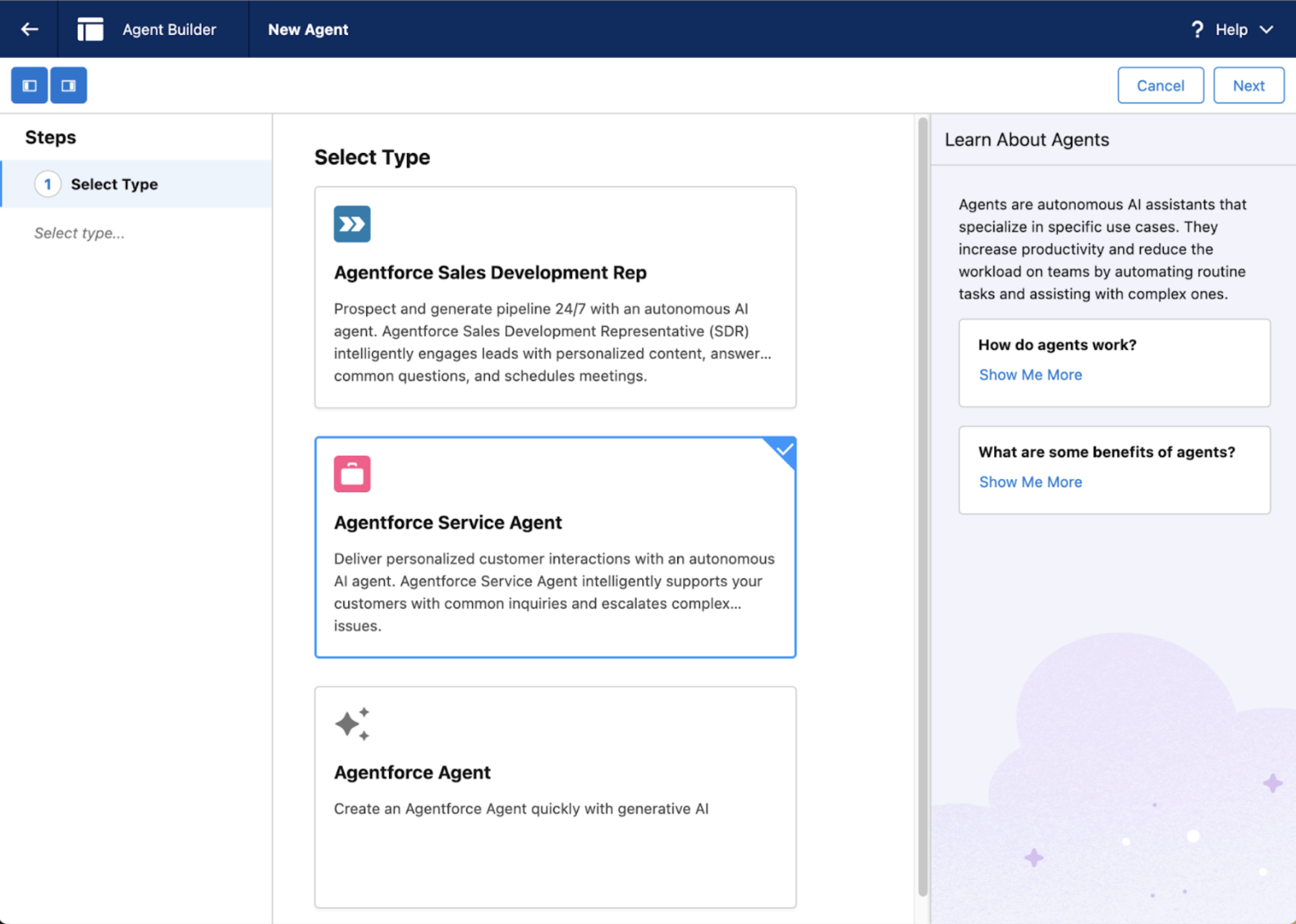
1. Go to Agents in the Quick Find box in Setup.
2. Click New Agent.
-
Select Type: Choose a preconfigured agent type that aligns with the skills your agent needs, or start from scratch.
-
Review Topics: Add or remove predefined topics, which are the categories of jobs an agent can do.
-
Define Settings: Name and describe your agent, define its role, and tell the agent about your company. Select an agent user that has the necessary permissions to access the information it needs to do its job.
-
Select Data: If Data Cloud is enabled in your org, you can choose to upload data like your knowledge articles, or other information for your agents. However, many kinds of agents don’t require data at all.
Once you finish the fourth step and click Create, voila! You have a new agent!
AI & Reasoning
The Reasoning Engine is the core intelligence behind Agentforce’s conversational behavior. It interprets user input, evaluates context, and dynamically determines what the agent should do next — all in real time.
Key Functions Of The Reasoning Engine:
-
Intent Matching: When a user types a request, the engine compares their input to the trigger phrases of all topics using semantic similarity — not just keywords. It chooses the best-fit topic based on meaning, not exact wording.
-
Context Awareness: The engine keeps track of the conversation history and available data (e.g., what actions have already run, which variables are filled) to avoid redundant questions or steps.
-
Instruction-Adherent: It continuously evaluates Instructions and ensures the agent adheres to the behavior you've defined. For example, if you instruct the agent to “never show internal data,” the engine will suppress that output even if a prompt tries to include it.
-
Fallback Strategy: If the input doesn’t match any topic confidently, the engine can:
1. Ask a clarifying question
2. Trigger a fallback or general assistance topic
3. Escalate to a human agent (based on logic)
-
Multi-Topic Handling: If a user’s input could match multiple topics, the engine selects the most contextually relevant one using ranking algorithms and usage data.
Testing & Preview
From within Agent Builder:
-
Use Preview & Test to simulate a full conversation.
-
See how the agent chooses topics and prompts.
-
View live data from Action Step executions.
-
Refine prompt output and topic logic based on test input.
Example Topic Flow
Here’s a basic structure of a Topic called "Check Case Status":
1. Agent Message: “Sure, I can help with that. What's your Case Number?”
2. Action Step: Run SOQL to find the Case by number.
3. Agent Response: Use a prompt to say “Your case is currently {Status}.”
4. Summary Step: “Let me know if you'd like help with anything else.”
Connecting To Channels
Once built and tested, the agent can be deployed via:
-
Einstein Copilot
-
Slack or custom chat interfaces
-
Embedded UI components
The same agent logic can be reused across interfaces for consistent behavior.
Final Thoughts
Salesforce Agentforce represents a significant leap forward in the world of customer service and automation. By combining AI-driven reasoning, dynamic topic handling, and seamless integrations with Salesforce's powerful platform, Agentforce empowers businesses to scale their support operations without sacrificing personalization or efficiency.
As automation continues to play a crucial role in modern customer service, adopting it allows organizations to stay ahead of the curve. By automating repetitive tasks, speeding up response times, and personalizing every interaction, Agentforce makes it easier than ever to deliver exceptional customer service.
If you're ready to explore how Agentforce can transform your support operations, start building with Agentforce today and reimagine what’s possible for your support teams.